Tesla Production and the Impact of US Tariff Plans
Introduction
The automotive industry has entered a period of significant transition, with electric vehicles (EVs) gaining market share and global trade policies shifting dramatically. At the center of this transformation stands Tesla, the world's largest EV manufacturer, which now finds itself navigating the complex implications of President Trump's recently announced 25% import tariffs on foreign cars and auto parts. This article examines Tesla's production capabilities, its unique position in the automotive market, and how the new tariff regime is likely to impact its operations and sales performance.
Tesla's Global Manufacturing Footprint
Tesla has established a formidable global manufacturing presence since its first Model S rolled off the assembly line at the Fremont factory in 2012. Today, the company operates production facilities across three continents with over 30 million square feet of factory space and a global workforce exceeding 70,000 employees.
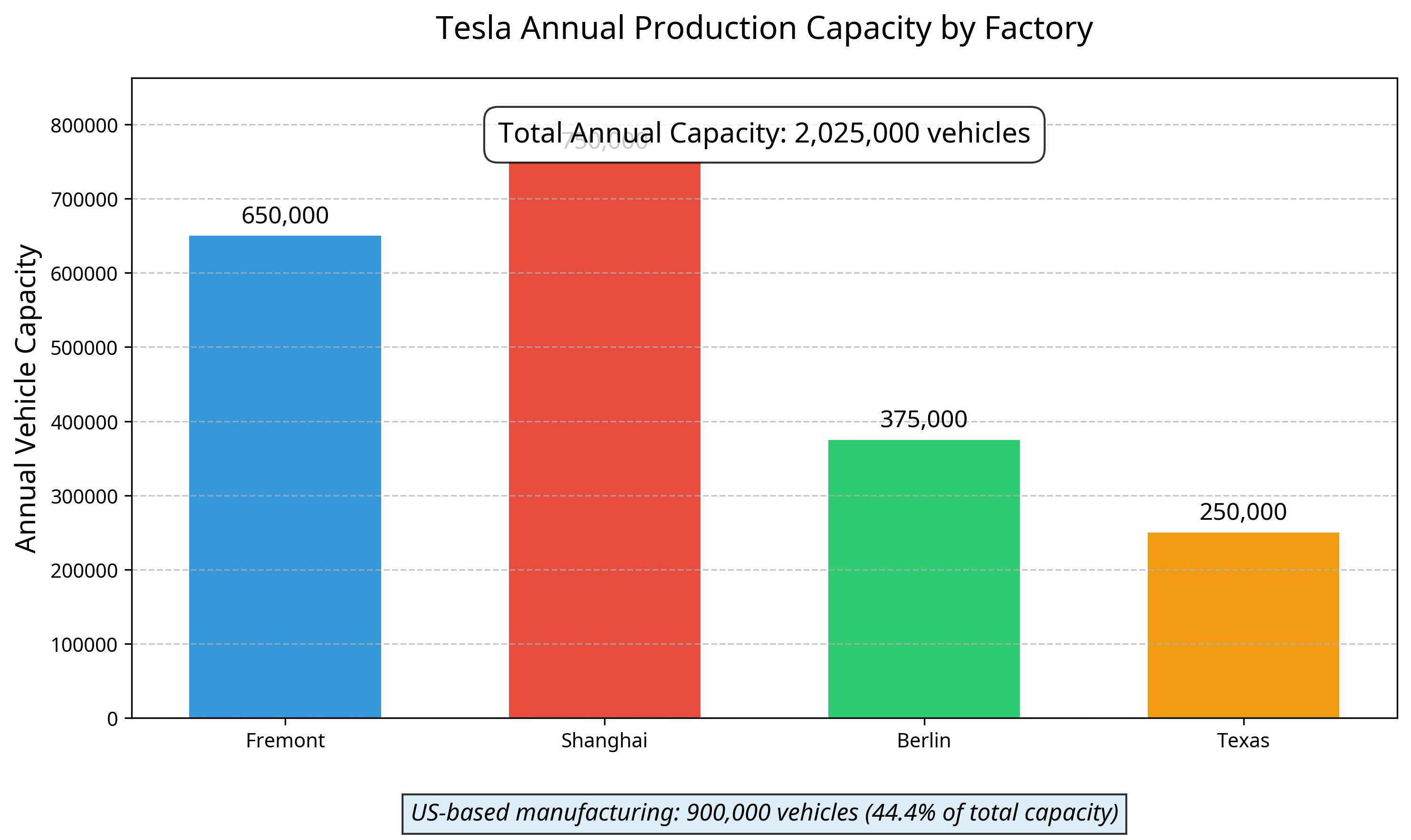
As shown in the visualization above, Tesla's annual production capacity is distributed across four major factories, with a total capacity exceeding 2 million vehicles annually. Notably, 44.4% of this capacity is located within the United States (Fremont and Texas factories), which has significant implications for the company's exposure to import tariffs.
US Manufacturing Facilities
Fremont Factory (California): Tesla's original manufacturing facility produces Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y vehicles. With a production capacity of up to 650,000 vehicles annually (550,000 Model 3/Y and 100,000 Model S/X), this factory remains central to Tesla's domestic production strategy.
Gigafactory Texas: Serving as Tesla's global headquarters, this facility has a production capacity exceeding 250,000 vehicles per year. It currently produces the Model Y and is slated to be the future home of Cybertruck production. In May 2023, the plant achieved a production rate of 5,000 Model Y units per week. Notably, this factory produces vehicles with both 4680-type battery cells (with structural battery packs) and 2170-type cells.
Gigafactory Nevada: Operating in partnership with Panasonic, this facility is one of the world's highest volume plants for electric motors, batteries, and powertrains. Recent investments include a $3.6 billion expansion announced in early 2023 to produce 4680-type battery cells (100 GWh per year) and Tesla Semi trucks (with potential for approximately 50,000 units annually).
Other US Facilities: Tesla also operates the Kato Factory (responsible for battery development and pilot production), Gigafactory New York (producing Solar Roof, solar panels, and electrical components for Superchargers), and Megafactory Lathrop (optimized for building utility-scale Megapack batteries).
International Manufacturing Facilities
Gigafactory Shanghai (China): Tesla's first factory abroad has a production capacity exceeding 750,000 vehicles per year, manufacturing Model 3 and Model Y vehicles. This facility serves as Tesla's main export hub and has been operating near full capacity for several months.
Gigafactory Berlin-Brandenburg (Germany): Tesla's first European factory has a production capacity of 375,000 vehicles annually (recently increased from 350,000). It currently produces the Model Y powered by 2170-type cells, with future plans to incorporate 4680-type cells.
Recent US Tariff Policies
On March 26-27, 2025, President Trump announced a 25% import tariff on foreign cars and auto parts, effective April 2, 2025. This policy represents a significant escalation in global trade tensions and has far-reaching implications for the automotive industry.
The tariffs apply to:
- All cars not manufactured in the United States
- Foreign-made auto parts
- Vehicles from major automotive exporters including Germany, Japan, and South Korea
- US-assembled vehicles that use significant quantities of foreign-made parts
This policy is part of a broader global trade strategy launched at the beginning of President Trump's second term. When announcing the tariffs, he stated: "What we're going to be doing is a 25% tariff on all cars that are not made in the United States. If they're made in the United States, it is absolutely no tariff."
Tesla's Sales Performance
Tesla's recent sales performance provides important context for understanding the potential impact of the new tariffs:
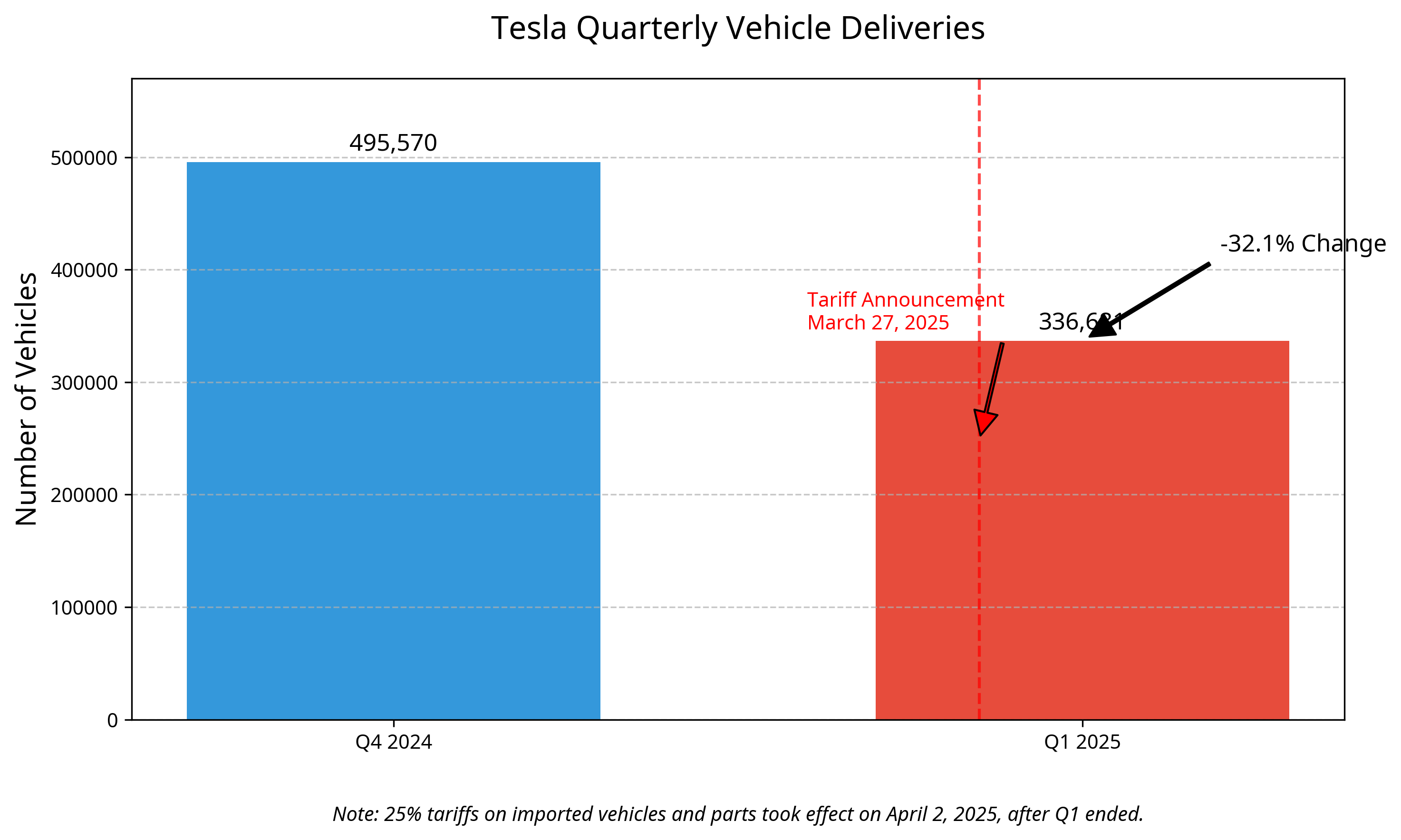
As illustrated in the chart above, Tesla experienced a significant 32.1% decline in deliveries between Q4 2024 and Q1 2025, with the tariff announcement coming just days before the end of Q1. While the tariffs themselves took effect after the quarter ended, the announcement may have influenced market sentiment.
Q1 2025 (January-March 2025)
- Production: 362,615 vehicles
- Deliveries: 336,681 vehicles (323,800 Model 3/Y and 12,881 other models)
- Year-over-year change: 13% decline from Q1 2024
- Quarter-over-quarter change: 32.1% decline from Q4 2024
Tesla attributed part of this decline to "changeover of Model Y lines across all four factories," which "led to the loss of several weeks of production in Q1." However, the company noted that "the ramp of the New Model Y continues to go well."
Q4 2024 (October-December 2024)
- Production: 459,445 vehicles
- Deliveries: 495,570 vehicles (a record quarter)
- Full Year 2024: 1,789,226 vehicle deliveries (the company's first annual sales decline)
Regional Performance
- European sales declined 49% in the first two months of Q1 2025
- Sales dropped particularly sharply in Germany (76% decline) and in France, Italy, and Portugal (over 50% decline)
- Customer loyalty has shown political divergence, with repeat Tesla buyers in "blue states" falling to 65% at the end of 2024 from 72% the year before, while slightly increasing in "red states" from 47.6% to 48.2%
How Tariffs Impact Tesla: A Nuanced Analysis
The relationship between the new tariffs and Tesla's operations is complex, with both advantages and challenges for the company.
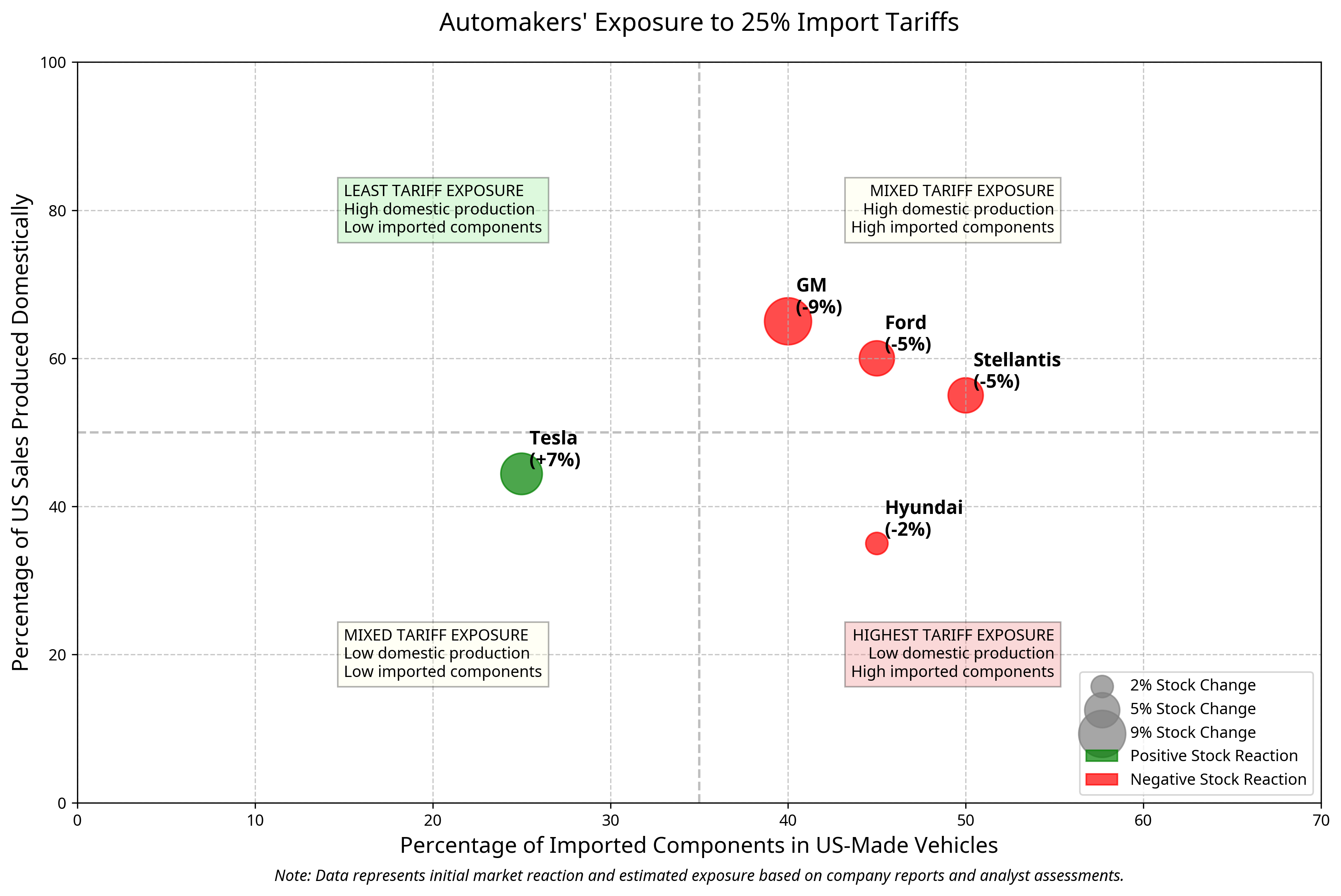
The visualization above illustrates the relative exposure of major automakers to the 25% import tariffs, based on two key factors: the percentage of US sales produced domestically and the percentage of imported components in US-made vehicles. The size and color of each bubble represent the initial stock market reaction following the tariff announcement.
Competitive Advantages
Domestic Manufacturing Focus: Tesla's strategy of manufacturing all vehicles sold in the US domestically (in Texas and California) provides significant insulation from the direct impact of the 25% tariffs on imported vehicles. As analyst Daniel Ives of Wedbush Securities noted, "Tesla would be less exposed to tariffs as their production and assembly is all in the US."
Supply Chain Integration: Compared to other automakers, Tesla manufactures more of its own parts domestically, including seats, motors, and other components. According to JP Morgan analysts, "Tesla in particular is known to source a greater proportion of components installed on its US-built vehicles in comparison to other automakers."
Market Positioning: The tariffs create a more challenging environment for Tesla's competitors, particularly those with significant manufacturing outside the US. CFRA Research stated that "among auto manufacturers and suppliers, we consider the most exposed to these tariffs to be 'Detroit Three' automakers GM, STLA, and F, as well as Canada-based auto supplier MGA, while TSLA screens as the least exposed."
Stock Market Response: The initial market reaction to the tariff announcement was positive for Tesla, with its stock rising as much as 7% while traditional automakers saw significant declines (GM down 9%, Ford and Volkswagen down about 5%). This indicates investor confidence in Tesla's relative position under the new tariff regime.
Significant Challenges
Component Imports: Despite its domestic focus, Tesla still imports 20-25% of components for its vehicles. According to a National Highway Traffic Safety Administration document from October 2024, between 60% to 75% of components for Tesla vehicles were made in the US or Canada, meaning a significant portion comes from other countries.
Financial Impact: Wolfe Research predicted a potential annual headwind of $1.6 billion for Tesla, primarily due to car components made in Mexico. Even Tesla CEO Elon Musk acknowledged, "The tariff impact on Tesla is still significant."
Supply Chain Competition: Mark Malek, Chief Investment Officer at Siebert Financial, pointed out a secondary effect: "Even Tesla, which manufactures most of its vehicles in the US, will pay more for parts because of competition amongst all manufacturers competing for the existing supply of non-tariffed parts, materials, and components."
International Retaliation: European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen called the US tariff move "bad for businesses, worse for consumers," while Germany's economic affairs Minister Robert Habeck indicated Europe would respond. Such retaliatory tariffs could impact Tesla's international sales, which include significant markets like China (8.8% of total sales in 2024) and Europe.
Confounding Factors Affecting Tesla's Performance
While tariffs will certainly impact Tesla's operations, several other significant factors are currently affecting the company's performance:
Political Backlash: Tesla has faced protests at its showrooms related to Elon Musk's role in the Trump administration, along with instances of vandalism against Tesla facilities, charging stations, and vehicles. A February 2025 poll by Morning Consult showed that 32% of US buyers "would not consider" buying a Tesla, up from 27% a year ago and 17% in 2021.
Production Transitions: Tesla cited the changeover of Model Y production lines across all four factories as causing several weeks of lost production in Q1 2025, which predated the tariff implementation.
Increased Competition: Chinese automaker BYD reported 416,000 EV sales in Q1 2025 (a 39% year-over-year increase), overtaking Tesla as the world's largest quarterly EV seller. BYD's advantages include lower prices and new fast-charging technology that can provide 250 miles of range after just five minutes of charging.
Potential Tax Credit Changes: President Trump has threatened to abolish tax credits for EV buyers. The combination of import tariffs and removal of tax credits could severely impact overall EV demand, regardless of manufacturing location.
Expert Perspectives on Tesla's Outlook
Industry analysts offer varying perspectives on how Tesla will navigate the tariff environment:
Daniel Ives of Wedbush Securities maintains an Outperform rating on Tesla with a $550 price target, despite describing Tesla's Q1 2025 deliveries as "a disaster for the bulls." Ives attributes Tesla's challenges primarily to brand issues related to Musk's political involvement rather than tariff impacts, stating: "This continues to be a moment of truth for Musk to navigate this brand tornado crisis moment and get onto the other side of this dark chapter for Tesla with much better days ahead."
Cornell University research professor Ian Greer sees potential benefits: "In the electric vehicle segment, tariffs are a boon to fiercely anti-union Tesla, which will benefit from the disarray of competitors (including the Big Three) who need time to rethink production strategies and retool factories."
CFRA Research and JP Morgan both position Tesla as the least exposed among major automakers to the negative impacts of tariffs, while Wolfe Research offers a more cautious assessment, highlighting the significant financial impact Tesla will still face.
Conclusion: Short and Long-Term Implications
In the short term, Tesla appears better positioned than many competitors to weather the impact of the new tariffs due to its domestic manufacturing focus and vertical integration. The company's stock initially responded positively to the tariff announcement, reflecting investor confidence in its relative advantage.
However, the 13% year-over-year sales decline in Q1 2025 indicates that Tesla faces significant challenges beyond tariffs, particularly related to political backlash against CEO Elon Musk and increasing global competition. The tariffs may provide some competitive insulation in the US market, but they won't resolve these broader issues.
In the longer term, several key factors will determine how tariffs affect Tesla:
- Supply Chain Adaptation: Tesla's ability to further localize its supply chain and reduce dependence on imported components will be crucial for minimizing tariff impacts. With 44.4% of its manufacturing capacity already in the US, Tesla has a strong foundation to build upon.
- International Market Access: If other countries implement retaliatory tariffs, Tesla's sales in important markets like Europe and China could suffer, potentially offsetting domestic advantages. This is particularly concerning given Tesla's recent sales declines in European markets.
- EV Market Growth: If the combination of tariffs and potential removal of tax credits suppresses overall EV demand, Tesla could face a shrinking market despite its relative advantages over competitors. This could accelerate the company's need to diversify into other product categories.
- Brand Perception: Tesla's ability to navigate the political associations of its CEO while maintaining appeal across the consumer spectrum will be essential for sales recovery. The growing political divide in customer loyalty suggests this remains a significant challenge.
As the tariffs only took effect on April 2, 2025, after Q1 ended, Tesla's Q2 2025 results will provide better insight into the actual impact of tariffs on the company's performance. The coming months will reveal whether Tesla can leverage its domestic manufacturing advantage to regain sales momentum or if broader market and political factors will continue to present significant headwinds.



0 Comments